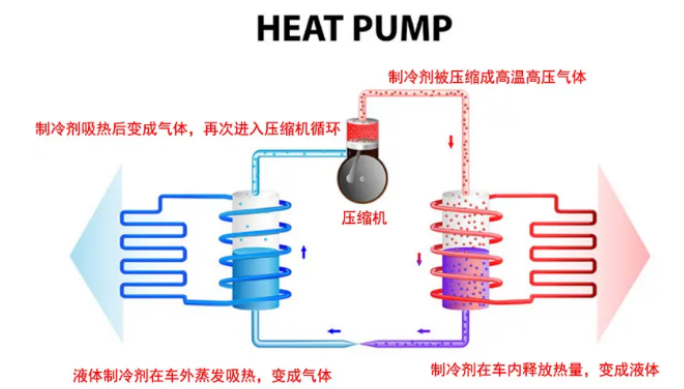
Now many electric vehicles have begun to use heat pump heating, the principle and air conditioning heating is the same, electric energy does not need to generate heat, but transfer heat. One part of electricity consumed can transfer more than one part of heat energy, so it saves electricity than PTC heaters.
Although heat pump technology and air conditioning refrigeration are transferred heat, but electric vehicle heating air consumption is still higher than air conditioning, this is why? In fact, there are two root causes of the problem:
1, need to adjust the temperature difference
Assume that the temperature the human body feels comfortable is 25 degrees Celsius, the temperature outside the car in summer is 40 degrees Celsius, and the temperature outside the car in winter is 0 degrees Celsius.
It is obvious that if you want to reduce the temperature in the car to 25 degrees Celsius in summer, the temperature difference that the air conditioner needs to adjust is only 15 degrees Celsius. In winter, the air conditioner wants to heat up the car to 25 degrees Celsius, and the temperature difference needs to be adjusted as high as 25 degrees Celsius, the workload is significantly higher, and the power consumption naturally increases.
2, heat transfer efficiency is different
The heat transfer efficiency is high when the air conditioner is turned on
In summer, car air conditioning is responsible for transferring the heat inside the car to the outside of the car, so that the car will become cooler.
When the air conditioner works, the compressor compresses the refrigerant into a high pressure gas of about 70 ° C, and then comes to the condenser located at the front. Here, the air conditioner fan drives the air to flow through the condenser, taking away the heat of the refrigerant, and the temperature of the refrigerant is reduced to about 40 ° C, and it becomes a high-pressure liquid. The liquid refrigerant is then sprayed through a small hole into the evaporator located under the center console, where it begins to evaporate and absorb a lot of heat, and eventually becomes a gas into the compressor for the next cycle.
When the refrigerant is released outside the car, the ambient temperature is 40 degrees Celsius, the refrigerant temperature is 70 degrees Celsius, and the temperature difference is as high as 30 degrees Celsius. When the refrigerant absorbs heat in the car, the temperature is lower than 0 degrees Celsius, and the temperature difference with the air in the car is also very large. It can be seen that the efficiency of the refrigerant's heat absorption in the car and the temperature difference between the environment and the heat release outside the car are very large, so that the efficiency of each heat absorption or heat release will be higher, so that more power is saved.
The heat transfer efficiency is low when the warm air is turned on
When the warm air is turned on, the situation is completely opposite to that of refrigeration, and the gaseous refrigerant that is compressed into high temperature and high pressure will first enter the heat exchanger in the car, where the heat is released. After the heat is released, the refrigerant becomes a liquid and flows to the front heat exchanger to evaporate and absorb the heat in the environment.
The winter temperature itself is very low, and the refrigerant can only reduce the evaporation temperature if it wants to improve the heat exchange efficiency. For example, if the temperature is 0 degrees Celsius, the refrigerant needs to evaporate below zero degrees Celsius if it wants to absorb enough heat from the environment. This will cause the water vapor in the air to frost when it is cold and adhere to the surface of the heat exchanger, which will not only reduce the heat exchange efficiency, but also completely block the heat exchanger if the frost is serious, so that the refrigerant can not absorb heat from the environment. At this time, the air conditioning system can only enter the defrosting mode, and the compressed high temperature and high pressure refrigerant is transported to the outside of the car again, and the heat is used to melt the frost again. In this way, the heat exchange efficiency is greatly reduced, and the power consumption is naturally higher.
Therefore, the lower the temperature in winter, the more electric vehicles turn on the warm air. Coupled with the low temperature in winter, the battery activity is reduced, and its range attenuation is even more obvious.
Post time: Mar-09-2024